ClimPACT2
4. Calculating the indices from netCDF data
Users who have three-dimensional netCDF datasets (time x latitude x longitude) of daily temperature and precipitation may utilise the climpact2.ncdf.wrapper.r and climpact2.ncdf.thresholds.wrapper.r scripts to calculate the ClimPACT2 indices. This functionality is intended for users familiar with R and the unix command line. This functionality is only available to users of Linux and MacOS operating systems. It utilises two packages developed by the Pacific Climate Impacts Consortium (PCIC): ncdf.helpers and climdex.pcic.ncdf. The latter package has been modified from it's original form in order to calculate all of the ClimPACT2 indices.
4.1 Installing required R packages
To calculate the ClimPACT2 indices on netCDF data your operating system will require the following software installed, in addition to R. All three products should be installable through your operating systems package manager. Select the versions of these packages that contain the development files. This process can be system dependent, please consult your technical support if you require help.
-
PROJ4 (libproj-dev package on Linux)
-
UDUNITS2 (libudunits2-dev package on Linux)
Once these products are installed on your operating system follow these steps:
-
cd to the climpact2-master directory created in Section 2
-
Enter R and run the following command source('installers/climpact2.ncdf.installer.r') to install the required R packages. This may take some time and you may be asked questions regarding the creation of a new library in which to install R packages to. You may also be asked to select the geographical location of the closest 'mirror' to download these packages from (see figure above). You may select any location, though the closest location will offer the fastest download speed. Lastly, you will also be asked whether you wish to install the modified climdex.pcic.ncdf package over any potentially existing package. This is necessary for calculating the indices on netCDF data. To do so, type "y" when asked.You will also be asked to confirm the installation of a modified version of climdex.pcic.ncdf. In order to proceed it is required that this modified R package be installed. It will overwrite any pre-existing copies of this package. The indices calculated in ClimPACT2 include those claculated by the original version of climdex.pcic.ncdf.
4.2 Calculating the indices on netCDF files
To calculate the ClimPACT2 indices on climate data contained inside one or more netCDF files, modify the climpact2.ncdf.wrapper.r script to point to these files and make necessary adjustments to the variable definitions in this script according to your data (the comments in this file will guide you in determining how to change these variables). As a test, it is recommended to run the above script on the provided sample data BEFORE running on your own data.
If you wish to calculate the indices for data contained in one set of netCDF files, however using percentile thresholds based on data in another set of netCDF files, then the climpact2.ncdf.thresholds.wrapper.r will need to be used. A typical example of this follows. The user has a netCDF file containing model simulated daily precipitation, maximum temperature and minimum temperature for the present day period of 1990 - 2010. The user also has a netCDF file containing climate model projections for the period 2050 - 2070. They wish to calculate the ClimPACT2 indices on both of these periods but want the percentile-based indices in both periods (present and future) to utilise thresholds calculated from the present day climate. For a brief explanation of climate indices refer to Appendix F (Wait, what is a climate index?).
This requires three steps:
-
Make a copy of climpact2.ncdf.wrapper.r and modify it to point to the present day netCDF files, specifying an appropriate base period. In the above example this might be 1990 - 2000 (your base period does NOT have to cover the entire range of your data). Run this script from the Linux command line using Rscript climpact2.ncdf.wrapper.r
-
Modify the climpact2.ncdf.thresholds.wrapper.r to point to the same present day netCDF files as specified in step 1. Here the user needs to specify the same base period, e.g. 1990 - 2000. Run this script from the Linux command line using Rscript climpact2.ncdf.thresholds.wrapper.r. Note step 1 and 2 can technically be done in any order, step 2 is only required in order to complete step 3.
-
Make a copy of climpact2.ncdf.wrapper.r and modify it to point to the future climate netCDF files, specifying a base period consistent with the above steps (e.g. 1990 - 2000) but this time specify the threshold file that was claculated in step 2 above. Run this script from the Linux command line using Rscript climpact2.ncdf.wrapper.r
These scripts typically take several hours to run (however, runtime varies strongly based on input file size and computer resources). Once you have run climpact2.ncdf.wrapper.r, numerous netCDF files will exist in the output directory specified. Where relevant, indices are calculated at both monthly and annual time scales. A typical output file name is r20mm_ETCCDI_ANN_climpact.sample_historical_NA_1991-2010.nc, where r20mm refers to the index calculated and ANN refers to the time scale this index was calculated on (MON for monthly). Output file names are dervied from the CMIP5 conventions and follow this format var_timeresolution_model_scenario_run_starttime-endtime.nc.
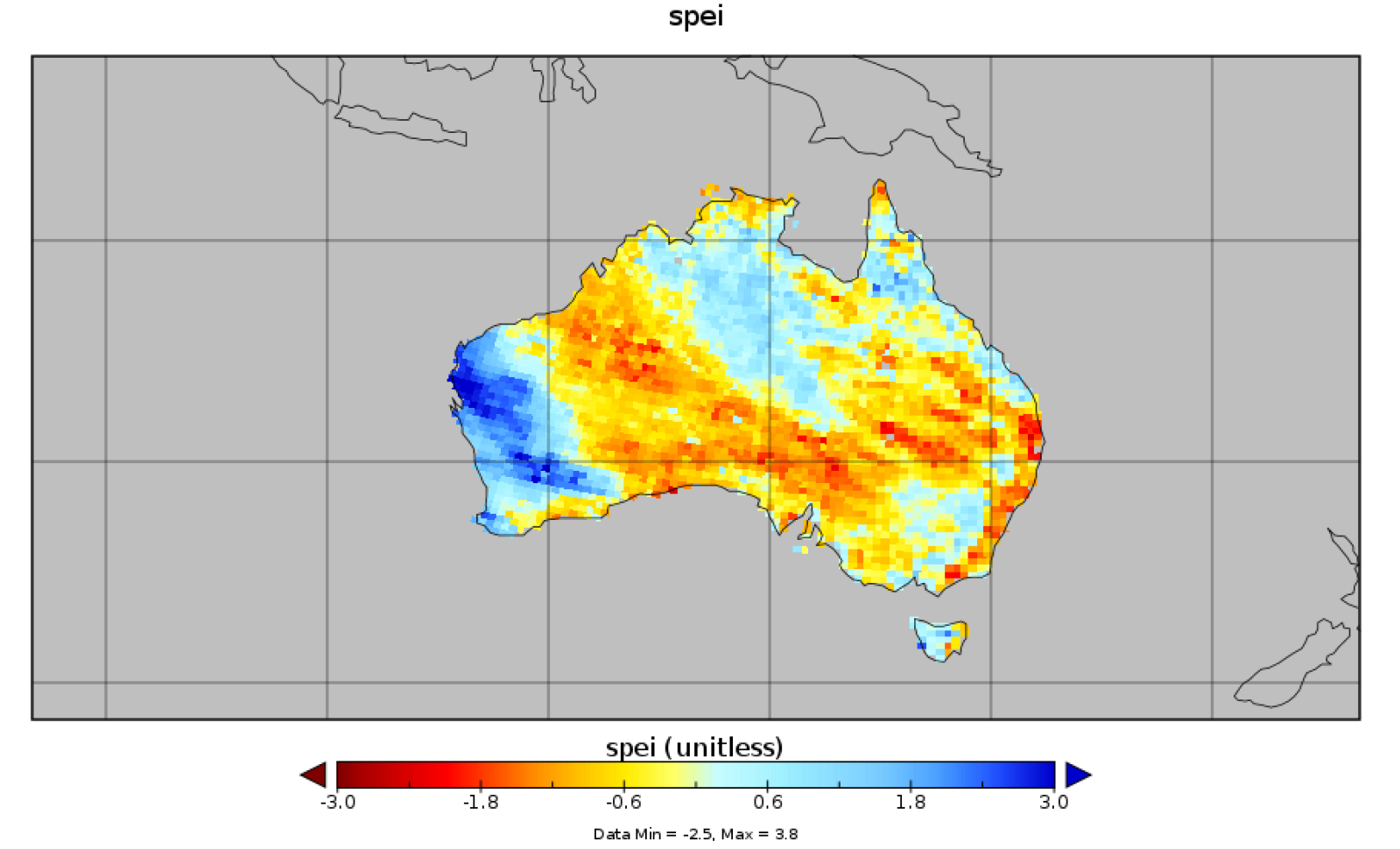
A visualisation of example output of the Standardised Precipitation-Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) calculated over Australia is shown below. We recommend using Ncview or Panoply for easily viewing netCDF output.